Isobornyl Methacrylate (IBOMA): Structure, Properties, and Industrial Applications
Release time:
2025-05-14
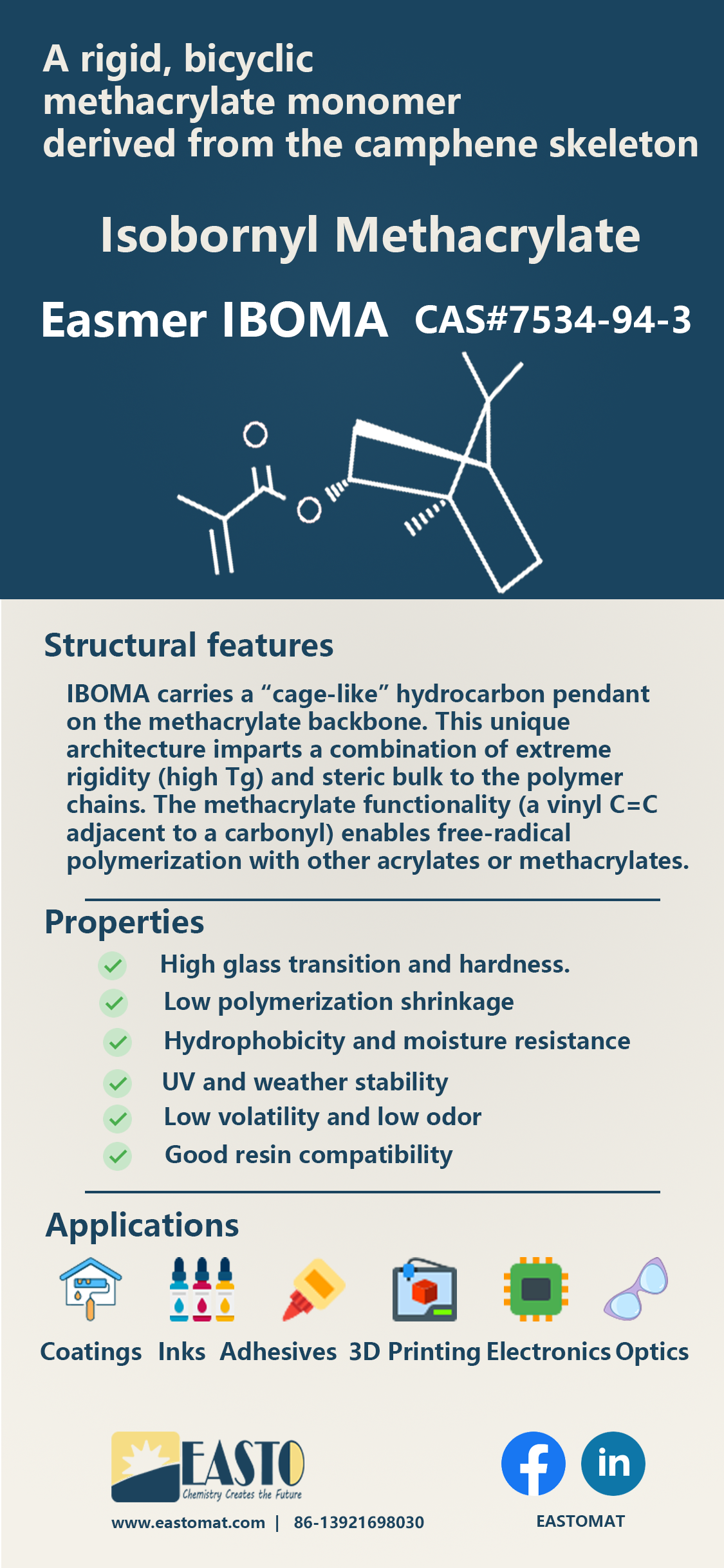
Isobornyl methacrylate (IBOMA, CAS 7534-94-3) is a rigid, bicyclic methacrylate monomer derived from the camphene skeleton. Its structure consists of a bulky, bridged bicyclic isobornyl side group attached via an ester linkage to a methacrylate double bond. In other words, IBOMA carries a “cage-like” (bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane) hydrocarbon pendant on the methacrylate backbone. This unique architecture imparts a combination of extreme rigidity (high glass-transition temperature) and steric bulk to the polymer chains. The methacrylate functionality (a vinyl C=C adjacent to a carbonyl) enables free-radical polymerization with other acrylates or methacrylates. In summary, IBOMA’s structure unites a polymerizable methacrylate group with a hydrophobic, bicyclic camphor-type side chain.
Key structural features: The isobornyl group is a bridged, nonpolar bicyclic hydrocarbon (trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptane) that provides exceptional steric hindrance and rigidity. The attached methacrylate ester brings the reactive C=C double bond (with a methyl on the α-carbon). Together these features yield a monomer that is chemically robust and forms high‐T_g polymers. The rigid cage group dramatically weakens inter-chain attraction (by introducing free volume) and imparts compatibility with many resin systems. In effect, IBOMA’s structure protects the polymer chain (spatial hindrance) and enhances resistance to degradation (UV, moisture, chemicals).
Structure–Property Relationships
The bulky bicyclic side chain of IBOMA directly translates into distinct polymer properties:
High glass transition and hardness. The rigid isobornyl moiety prevents chain mobility, yielding very high glass transition temperatures (T_g). Polymers of IBOMA are unusually hard and thermally stable. In fact, IBOMA is often added to acrylic formulations as a toughness agent, producing cured resins with high hardness and scratch resistance.
Low polymerization shrinkage. The large volume of the isobornyl group counteracts the volume collapse typically seen in polymer curing. IBOMA-based resins exhibit significantly reduced shrinkage during polymerization. This is a key benefit in precision applications (dental resins, optical adhesives, etc.), where dimensional stability is critical.
Hydrophobicity and moisture resistance. Being a nonpolar hydrocarbon, the isobornyl group makes IBOMA very hydrophobic. Coatings or polymers containing IBOMA repel water and resist humidity. This water‐resistance arises because the large bicyclic group disrupts hydrogen bonding and polar interactions at the surface.
UV and weather stability. The same steric hindrance that protects against moisture also shields the polymer from UV radiation and oxidative aging. The bicyclic cage effectively scavenges (or blocks) free radicals, so IBOMA-containing coatings yellow more slowly and maintain gloss outdoors. In practice, IBOMA enhances the light‐fastness and long-term weatherability of acrylic and UV-cured systems.
Low volatility and low odor. IBOMA has a low vapor pressure and is not very volatile. In formulations it acts as a reactive diluent (not a traditional solvent), reducing viscosity without high VOC content. Its low volatility also means low odor and low skin and respiratory irritation compared to many acrylates.
Good resin compatibility. Despite its rigidity, the IBOMA monomer dissolves easily in common acrylic, polyester, and alkyd resins. It often improves flow and leveling of formulations by reducing intermolecular forces in the mixture. In UV formulations, IBOMA mixes well with other oligomers and acrylates, enabling high-solid or solvent-free coatings.
In short, IBOMA’s bicyclic structure endows cured materials with a unique balance of hardness and toughness, combined with hydrophobicity and stability (UV/moisture). These characteristics (often listed as “hardness, high Tg, water resistance, low yellowing, etc.”) make it a valuable specialty monomer.
Applications in Coatings, Adhesives, Inks, and Optics
Because of its favorable properties, IBOMA is used widely across industries. The main application areas are:
High-performance coatings. IBOMA is added to solventborne and UV‐curable coatings to improve durability. In clear and pigmented coatings, it boosts film hardness, abrasion/scratch resistance, and chemical resistance. It also raises gloss and improves leveling, yielding smooth, shiny surfaces. In solvent-free and high-solids formulations, IBOMA lowers viscosity as a reactive diluent (reducing VOCs) while curing into the film. The end result is a coating with enhanced weatherability (resistance to yellowing and moisture) and adhesion.
Key benefits in coatings: high hardness and gloss, improved adhesion, low shrinkage (better film integrity), UV‐stability and water resistance.
Adhesives (structural and PSA). IBOMA is used in acrylic and methacrylate adhesive formulations (two-part structural adhesives, pressure-sensitive tapes, etc.). Its rigid structure helps produce an adhesive with high bonding strength and high shear/peel resistance. IBOMA-containing adhesives typically exhibit excellent adhesion to a variety of substrates (metals, plastics, composites). The high T_g contribution also means the cured adhesive remains solid and heat-resistant at higher temperatures. In addition, the hydrophobic nature improves moisture resistance of the bond line. For many structural adhesives, IBOMA enables high-gap-filling formulations with low cure shrinkage and low odor (thanks to its low volatility).
Key benefits in adhesives: improved bond strength and toughness, high-temperature performance (heat resistance), low shrinkage (for dimensional stability), and low odor/low VOC compared to conventional solvents.
Printing inks. In UV-curable ink formulations (inkjet, screen, flexo), IBOMA acts as a reactive diluent that enables rapid curing with minimal distortion. It helps the ink flow smoothly (good leveling) and cure to a tough, clear film. IBOMA improves adhesion of inks to difficult substrates (plastic films, laminates, etc.) and enhances abrasion and chemical resistance of the print. Because of its low volatility, IBOMA-based inks have low odor and reduced VOC. Its UV-stable nature also means printed colors maintain their brightness over time (less yellowing).
Key benefits in inks: fast cure under UV, strong inter-coat adhesion, high durability of the print (scratch/chemical resistance), excellent color clarity and retention.
Optical materials and adhesives. IBOMA is attractive in optical polymers and adhesives (lenses, waveguides, fiber optics) because it yields clear, high-refractive-index polymers with low internal stress. Its transparency and ability to suppress haze produce optically clear materials. The rigid cage structure raises the polymer’s refractive index (useful for matching glass or improving lens performance) and enhances dimensional stability (low thermal expansion). In optical adhesives, IBOMA provides bonds that are strong yet do not yellow with UV exposure. Overall, IBOMA-based formulations deliver the durability (hardness, moisture resistance) needed for outdoor or demanding optical applications.
Key benefits in optics: high optical clarity and gloss, higher refractive index, low stress/shrinkage (good dimensional control), long-term UV stability.
Additional applications include wood and plastic coatings (IBOMA imparts water repellency and hardness), 3D-printing resins (enabling rigid printed parts), and even specialty areas like dental resins or medical polymers (where low shrinkage and biocompatibility are valued). Across all uses, IBOMA’s blend of high performance and low volatility make it especially valuable as a reactive diluent in sustainable, high-solid formulations.
In summary, the rigid bicyclic structure and methacrylate functionality of IBOMA provide a rare combination of properties. Polymers and formulations containing IBOMA exhibit low curing shrinkage, high hardness, strong hydrophobicity, and excellent weather and UV resistance. These attributes make IBOMA a go-to monomer for professionals seeking durable, high-performance acrylic resins in coatings, adhesives, inks, and optical materials. Its use leads to tougher, longer-lasting products – for example, scratch-resistant industrial coatings, high-strength structural adhesives, fade-resistant printed inks, and optically clear polymers – all supported by extensive industry experience.
Latest News
Get a Free Consultancy
NANTONG EASTO MATERIALS TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD.

No.118,Zhujiang Rd.,Juegang St.,Rudong County,
Nantong City,Jiangsu Province,226400,China




 2025-05-14
2025-05-14