Hydroxy Acrylates: Key Reactive Monomers for High-Performance UV/EB Curing Formulations
Release time:
2025-07-16
In the field of photocuring materials, particularly in UV/EB curing systems, the selection of reactive monomers directly impacts the performance of end products such as coatings, inks, and adhesives.
Hydroxy Acrylates have gained increasing attention and adoption from formulators due to their excellent reactivity and unique functional group structure.
I. Structural Characteristics and Chemical Mechanism: Why is "Hydroxyl" So Important?
Hydroxy acrylates are a class of monomers containing both a
hydroxyl group (–OH) and an acrylate group (–C(O)O–CH=CH₂). Their general chemical structure is typically:
HO–R–O–C(O)–CH=CH₂
Here, the R group can be an alkyl group, ether chain, polyether segment, ester chain, or even a polyfunctional structure, which leads to a wide variety of hydroxy acrylate types and diverse properties.
Their performance advantages primarily come from the synergistic effect of these two functional groups:
Polarity and Hydrogen Bonding of the Hydroxyl Group: The hydroxyl group has strong hydrophilicity and polarity. Before curing, it can improve the wettability, adhesion, and dispersion of the resin. After curing, it can enhance the scratch resistance, flexibility, and adhesion of the material by forming a hydrogen bond network structure.
High Reactivity of the Acrylate Group: The acrylate group can quickly participate in free radical-initiated photopolymerization reactions, enabling rapid cross-linking and curing, thereby improving production efficiency and reducing energy consumption.
Additionally, hydroxy acrylates can undergo further reactions with isocyanates and epoxy compounds to form polyurethane acrylates (PUA) or functional hybrid polymers, further expanding their structural design space and performance combination capabilities.
II. Application Value in the UV/EB Curing Industry
Thanks to their excellent wettability, reactivity, and polarity, hydroxy acrylates play multiple functional roles in the UV/EB curing field and are suitable for various niche markets.
UV Coatings: On substrates like plastics, metals, glass, and wood, hydroxy acrylates can enhance the adhesion between the primer layer and the substrate, with particularly significant effects on polar materials such as PET/PC/ABS. At the same time, they can improve the abrasion resistance and impact resistance of the surface coating.
UV Inks: By introducing an appropriate amount of hydroxy acrylate, the viscosity of the ink system can be adjusted, pigment wetting and dispersion can be improved, and printability (e.g., flexo, inkjet, screen printing) can be enhanced. Furthermore, the hydroxyl group can significantly boost the adhesion of the ink to the substrate (e.g., aluminum foil, film).
UV Adhesives: For structural adhesives or pressure-sensitive adhesive systems requiring flexibility, impact resistance, and humidity/heat resistance, hydroxy acrylates can co-crosslink with polyurethane prepolymers, increasing cross-linking density and interlayer adhesion.
3D Printing Photosensitive Resins: In photocurable 3D printing materials like those used in DLP/SLA, the introduction of hydroxy acrylates can improve the resin's flowability and the cured product's flexibility, while also imparting stronger mechanical bonding, which aids in inter-layer adhesion during printing.
III. Recommended Product Examples
The following are several commonly used hydroxy acrylate products, which are widely used in industrial formulation design due to their diverse structures and outstanding properties:
Product Name | Chemical Name | CAS No. | Structural Characteristics | Properties | Applications |
Easmer HEA | 2-Hydroxyethyl Acrylate | 818-61-1 | Linear molecule with one hydroxyl group and one acrylate group | Low viscosity, high reactivity, enhances adhesion and flexibility | UV coatings, inks, adhesives, reactive diluents, etc. |
Easmer HPA | 2-Hydroxypropyl Acrylate | 25584-83-2 | Similar structure to HEA, but the hydroxypropyl structure provides better flexibility | Low irritation, low viscosity, enhances product flexibility and toughness | UV inkjet inks, pressure-sensitive adhesives, elastic coatings, etc. |
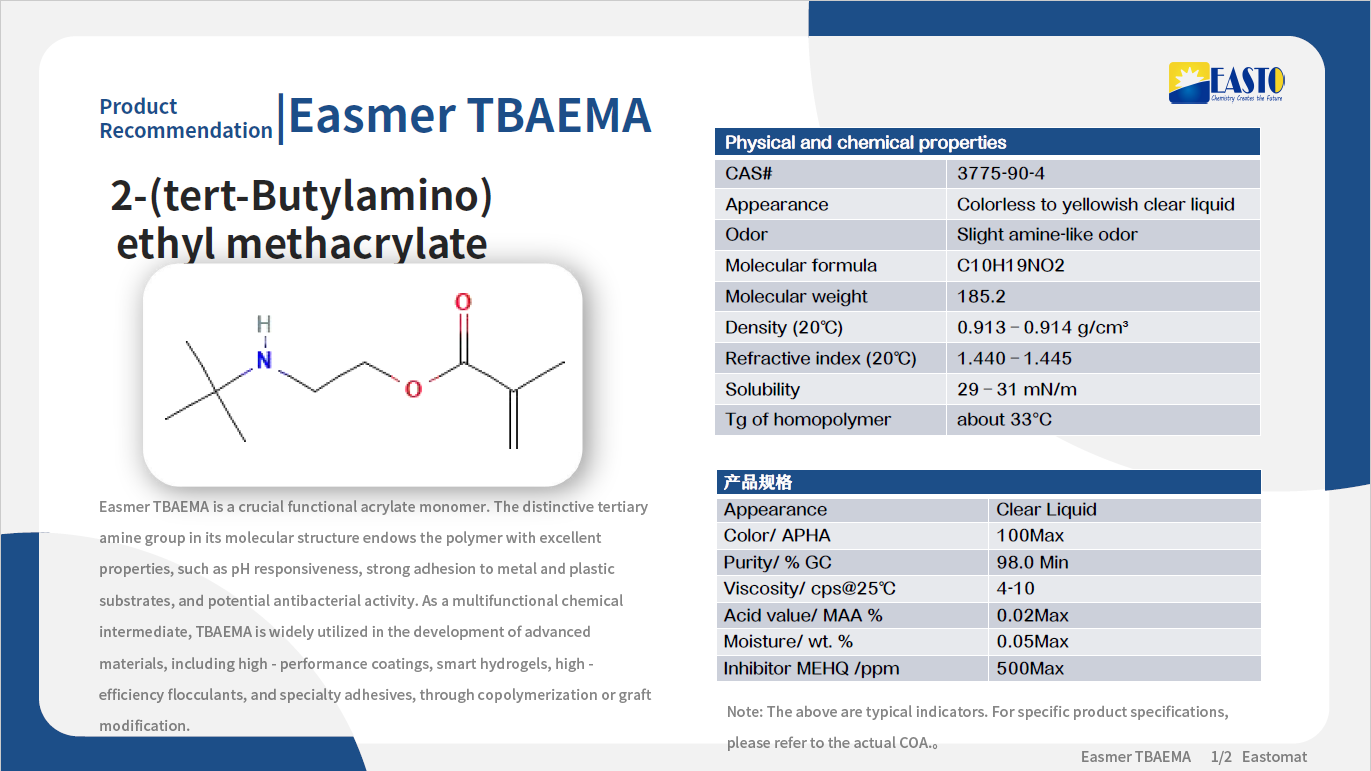
Easmer HEMA | 2-Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate | 868-77-9 | Similar to HEA, but it's a methacrylate structure, resulting in harder, more heat-resistant polymers after curing | Moderate reactivity, high mechanical strength, good adhesion properties | 3D printing, photocurable composite materials, medical coatings, etc. |
Easmer 4-HBA | 4-Hydroxybutyl Acrylate | 2478-10-6 | Has a longer alcohol chain segment, providing better flexibility and cohesive strength | Low irritation, good solubility and reactivity | Flexible coatings, elastic sealants, plastic primers, etc. |
IV. Conclusion: Small Molecule, Big Empowerment
Although hydroxy acrylate monomers are relatively simple in molecular structure, they play a triple role as a lubricant, binder, and reaction promoter in UV/EB curing systems. Through reasonable selection and structural matching, more precise material design and performance balance can be achieved for different substrates, mechanical properties, and curing efficiency requirements.
For formulators looking to enhance product performance, improve adhesion, or optimize processing performance, hydroxy acrylates are undoubtedly a class of key monomers worth in-depth study and flexible application.
For further technical parameters, formulation recommendations, or sample procurement of various hydroxy acrylates, please contact us for product technical data (TDS).
Previous Page
Next Page
Previous Page
Next Page
Latest News
Get a Free Consultancy
NANTONG EASTO MATERIALS TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD.

No.118,Zhujiang Rd.,Juegang St.,Rudong County,
Nantong City,Jiangsu Province,226400,China




 2025-07-16
2025-07-16