Three Major Technology Trends and Market Hotspots We've Observed.
Release time:
2025-08-04
I. Introduction: Beyond Efficiency, Towards a New Era
UV/EB curing technology has become an eco-friendly solution for coatings and inks due to its high efficiency and low VOC emissions. In 2025, the industry is undergoing a profound transformation, shifting from a simple pursuit of efficiency to a new era defined by sustainable development, technological innovation, and a reshaping of the global market. The integration of technology with ESG strategies and the circular economy, along with the convergence of forces like bio-based materials, carbon footprint accounting, and the popularization of UV LED, are redefining the future landscape.
II. Major Trend One: The Green Revolution – Sustainability as a Core Driver
The Rise of Bio-based and Biodegradable Materials
Commercial breakthroughs: Companies such as Arkema and Covestro have launched UV resins with bio-based content as high as 85% (e.g., the Sartomer® series), which are certified by ISCC PLUS and integrated into the global supply chain.
End-of-life management: RadTech established a "Biodegradable Materials Task Force," and a 2025 study confirmed that EB-cured inks perform exceptionally well in industrial composting, providing an environmentally friendly solution for food packaging.
Raw material innovation: Biomass sources like castor oil and lignin are being converted into high-performance polyurethane acrylates (PUA), which reduce carbon footprints and open up new material fields.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) and Carbon Footprint Quantification
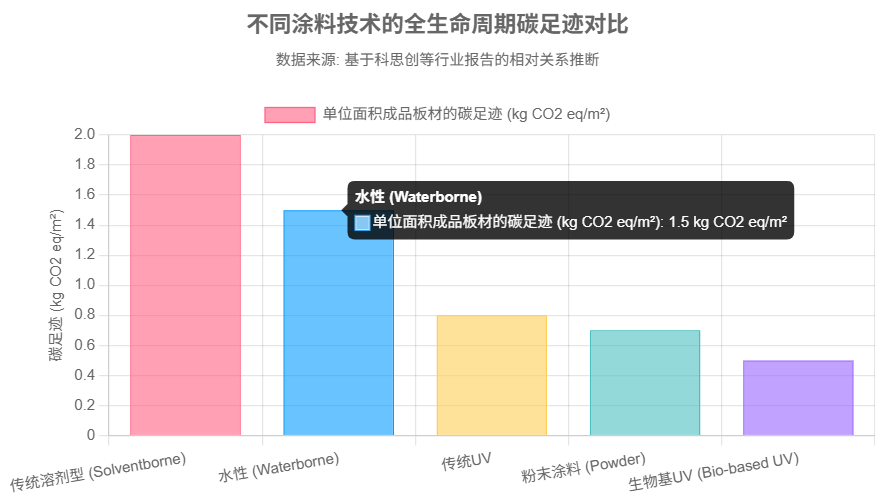
Data-driven decisions: LCA studies show that UV/EB technology can cut the carbon footprint of coil coating production in half compared to traditional processes.
Covestro's white paper: UV technology, especially when combined with bio-based resins, has significantly lower carbon emissions than solvent-based/water-based coatings, providing a clear basis for downstream carbon reduction.
Core value: LCA demonstrates that the advantages of UV/EB extend from production (low VOC/energy consumption) to the end product (biodegradability), making it a key pillar of ESG strategies.
Further Evolution in Energy Efficiency: The Complete Triumph of UV LED
Energy-saving revolution: UV LED can replace mercury lamps and save up to 85% of energy, thereby lowering the operational carbon footprint.
Technical advantages: These systems are ready to use instantly, are cool light sources suitable for heat-sensitive substrates like paper, and have no ozone emissions, which simplifies system design.
Industry impact: The transition to UV LED has become a necessary choice for increasing sustainable competitiveness in high-energy-consuming sectors like printing and coating.
III. Major Trend Two: Accelerating Technological Iteration – Comprehensive Innovation from Light Sources to Materials
A. The Competition and Integration of Light Sources
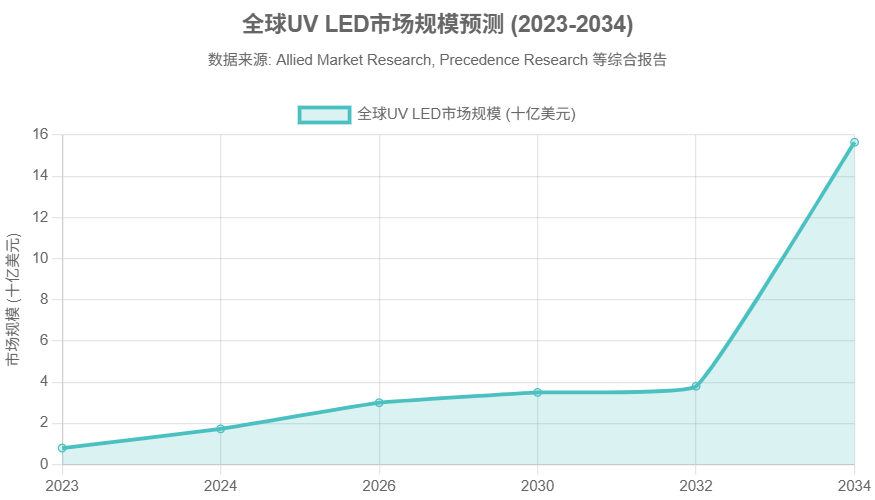
UV LED dominates the market: The market size is projected to grow from $800 million in 2023 to $3.8 billion in 2032, with a CAGR of 19.4%. Its advantages include a narrow wavelength that precisely matches photoinitiators, a lifespan of tens of thousands of hours, and low-temperature curing, making it suitable for precision manufacturing in electronics and medical fields.
Dual-Cure's transitional value: Ink formulations that are compatible with both mercury lamps and UV LEDs simplify the equipment upgrade path for companies and reduce inventory costs.
The irreplaceable nature of Electron Beam (EB): EB's advantages include not needing a photoinitiator (eliminating migration risks) and strong penetration, which allows for curing thick coatings and high-pigment systems. It is therefore suitable for food packaging and floor coatings. A current challenge is the high cost of equipment, which is driving the industry towards developing smaller, lower-cost EB systems.
Innovation in Hybrid Curing Systems: Combining UV pre-curing on the surface with EB deep curing solves the problem of oxygen inhibition, eliminating the need for nitrogen protection and achieving perfect curing of thick coatings.
B. Application-Driven Formulation Innovation
Evolution of high-performance resins: Epoxy acrylates are known for high hardness and chemical resistance, and are being modified to balance flexibility. Polyurethane acrylates (PUA) can be adjusted to create a range of materials from elastomers to tough coatings. Additives such as amine-modified polyether acrylates are driving fine-tuned performance control, including curing speed and resistance to yellowing.
Emerging application scenarios: In 3D printing, photocurable resins require low viscosity and high reactivity, with cured properties comparable to engineering plastics (e.g., Arkema's collaboration with HP/Stratasys). In the automotive and electronics industries, UV/EB is used for car headlight reflectors and PCB solder masks to achieve lightweighting and low-temperature, rapid curing. For coil coatings, UV/EB challenges thermosetting processes by offering high-speed, low-carbon solutions for metal decoration.
Technological synergy: Advances in light sources, such as the widespread adoption of UV LED, drive the development of new formulations, while high-performance resins, in turn, facilitate the penetration of light source technology into high-value sectors.
IV. Major Trend Three: Reshaping the Market Landscape – Emerging Markets and Global Supply Chain Challenges
Market Growth and Regional Shifts
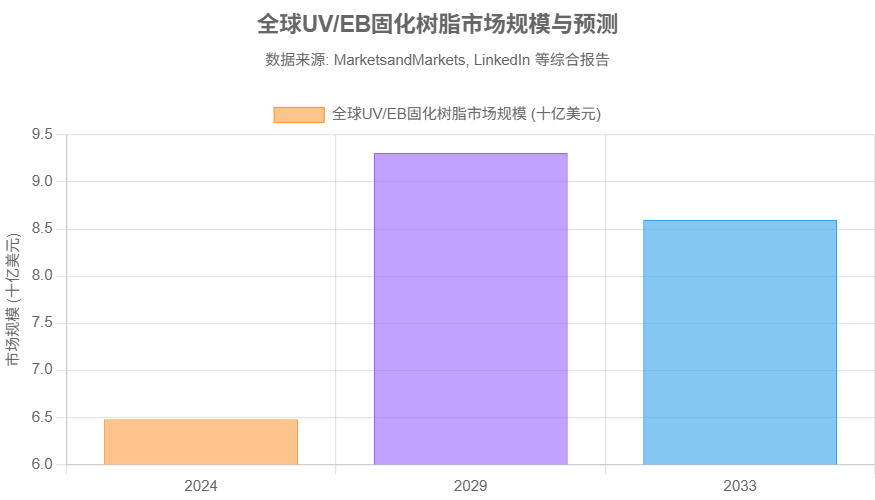
The global UV/EB resin market is expected to reach $8.6–10.6 billion by 2033, with a CAGR of 7–8.5%.
The Asia-Pacific region dominates this growth, accounting for 40% of the global market share in 2023. Driving factors include:
China's manufacturing base in electronics, automotive, and printing.
The demand for high-performance materials from the new energy vehicle and semiconductor industries.
Strong policy push for VOC reduction, which encourages the transition from solvent-based to UV/EB technology.
The maturity of the local supply chain, which lowers costs.
The "Achilles' Heel" of the Supply Chain
Trade protectionism: Increasing global trade uncertainty impacts the stability of the supply chain.
Specialty monomers/oligomers: High technical barriers and concentrated suppliers increase supply risks.
Logistics costs: Global transportation disruptions have driven up raw material costs.
Complex Global Regulatory Environment
Compliance as a competitive advantage: This includes regulations such as the EU's REACH, EFSA food contact standards , the US FDA's FCN certification , and China's MEE/NMPA regulations.
Companies must make proactive investments in compliance (e.g., toxicology research, migration testing) to enter sensitive markets like food and medical products.
Opportunities Amid Challenges
The risks associated with photoinitiators are driving the development of EB and cationic curing.
Cost pressures are encouraging the development of highly reactive resins, which reduces the required amount of initiators.
Stringent regulations are leading to innovations in low-migration and bio-based materials.
V. Conclusion: Integration and Synergy
The three major trends form an organic whole for the industry's development. Sustainability acts as the rudder, setting the direction for low-carbon and green materials. Technological innovation serves as the engine, with hardware (UV LED/EB) and software (high-performance resins) working together to push the boundaries of applications. Market dynamics represent the road conditions, with growth in the Asia-Pacific region providing opportunities, while supply chain and regulatory challenges require proactive responses. The future belongs to companies that can integrate these three elements: meeting sustainable standards, possessing technical performance and cost-effectiveness, and being flexible in responding to global fluctuations. Collaborative innovation across the entire value chain will be the key path to leading UV/EB into the next decade.
*This article condenses key insights based on industry technical white papers, market reports, and corporate case studies (from Arkema, Covestro, and RadTech, among others). It retains crucial data and logical chains.
Previous Page
Latest News
Get a Free Consultancy
NANTONG EASTO MATERIALS TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD.

No.118,Zhujiang Rd.,Juegang St.,Rudong County,
Nantong City,Jiangsu Province,226400,China




 2025-08-04
2025-08-04